Redis HA on Kubernetes
I recently had an oppurtunity to setup redis HA on Kubernetes. This was done using the redis-ha stable helm chart. This blog contains details on how the default installation works, observations and few tweaks done to meet our requirements.
Note: Check README of the redis-ha chart for installation instructions.
Redis-HA Components
The typical components required for Redis-HA setup
- Redis
- The KV store
- One takes the responsibility of Master
- The Replicas syncs data from master using
replicaofcommand.
- Sentinel
- Responsible to trigger replication on slaves
- Failure detection
- Automatic Failover
- Shipped as
redis-sentinel - Sentinel can be queried on which instance is master.
- Proxy
- A redis “Master” aware proxy
- Routes connections to actual master by querying sentinel.
- The chart uses HAProxy (with appropriate configurations) as the proxy layer.
For more reading on redis replication.
On Kubernetes
- Redis runs as Statefulsets with Sentinel as Sidecar
- HAProxy runs as Deployment with static configuration.
Visualizing it,
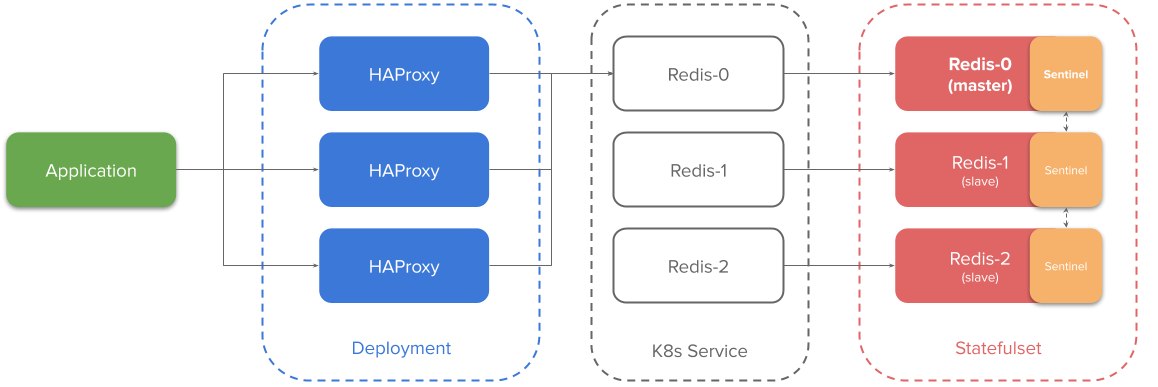
Explaining the above setup,
- The application connects to HAProxy instances (through Kuberentes Service or Pod IPs of HAProxy)
- Each replica of the statefulset has a Kubernetes Service exposed for it. The chart terms it “announce” service. The sole reason for the announce service is they have one Cluster IP/DNS name through which the HAproxy can query the sentinel on which instance is master and route connections to the instance.
- HAProxy finds master by querying sentinel
SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-nameand also queries redis instance withinfo replicationand “grep"ping for the string “role:master” - Each statefulset replica has redis running on port
6379and sentinel running on port26379.
It is important that we run atleast 3 instances. For more information on redis-sentinel setup & failover, check this documentation. Configurations like down-after-milliseconds, failover-timeout need to be configured accordingly for your setup.
Issues
Personally, I had 2 issues with the above setup.
-
Sentinel and Redis pods are coupled together. This means if a node stops responding, the redis and the sentinel pod goes unresponsive together. The sentinel could might as well be a separate component so that failover can be done independently. However, the setup described in Redis official docs is what the chart implements. We felt pulling out the sentinel out of the statefulset as a deployment required lots of effort, and hence went with what came with the chart.
-
Performance impact due to additional hops. The HAProxy uses static Cluster IP to route traffic to the master instance. This meant the following hops: App to HAProxy, HAProxy to Kuberentes Service, Redis Pod IP. We wanted to try an alternative to make HAProxy reach out to Pod IP directly without the need for a NAT (read Kuberentes Service) in-between.
Alternate Setup
We have Consul running on our clusters which is used for Service Discovery. The idea is
- Register pods of Statefulset to Consul
- Use consul-template to dynamically render HAProxy upstreams as Pod IP addresses directly (instead of the Kubernetes Service).
Performance analysis
redis-benchmark is a tool shipped with redis to measure performance.
## Test get and set operations
redis-benchmark -c 100 -t get,set -h ${HAPROXY_SVC_HOST}
3 Setups were tested.
- Redis Standalone
- Directly connected via Pod IP
- Redis HA as per default chart
- HAProxy upstreams as Kubernetes Service of Redis instance.
- Redis HA using Consul Template
- HAProxy upstreams as Pod IP addresses Redis instance.
| Operation | Standalone | Redis HA with K8s Service | Redis HA with Pod IP |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 51599.59 ops | 37257.82 ops | 44014.08 ops |
| SET | 53734.55 ops | 34989.50 ops | 42247.57 ops |
ops: operations per second
As expected standalone tops the benchmark. However, skipping the kubernetes service does help us in more throughput.
Other thoughts
We had to register to consul the pods and use consul-template to dynamically render HAProxy configurations. There was no tool to watch on Kubernetes API and dynamically render templates based on status E.g watch endpoints API to render Pod IPs directly in HAProxy config. This gave the idea of kube-template. A template rendering tool that queries Kuberenetes API and also watches for changes and re-rendering when needed.